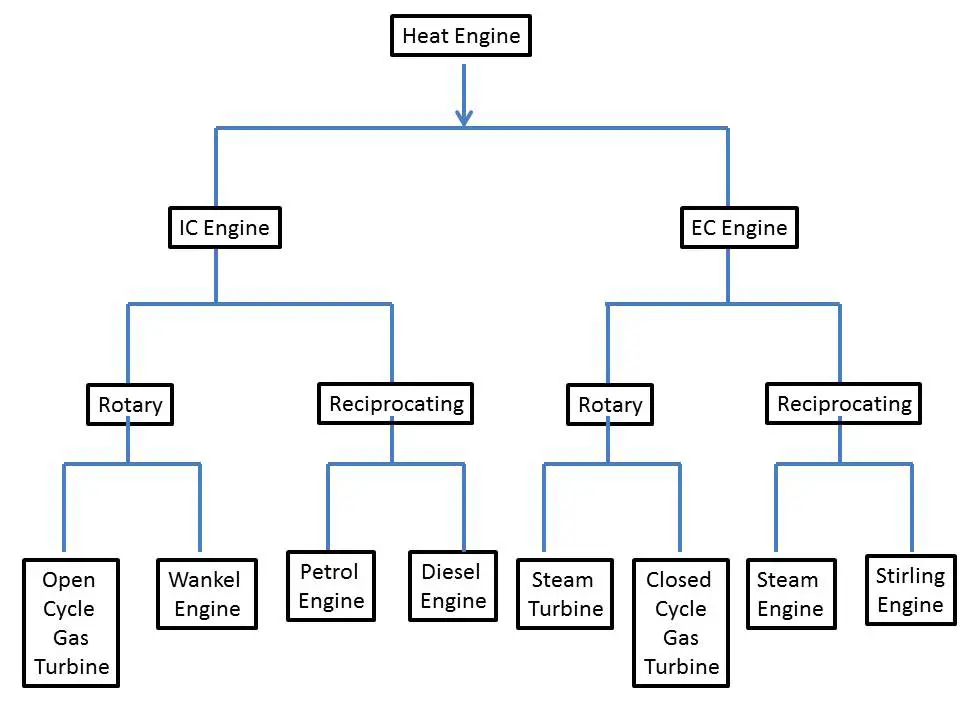
IC ENGINE BASIC Q/A

- The size of this engine is very less. ,
- These engines have a high power to weight ratio.
- This engine is good for applications which require small power.
- These engines are more portable.
- Very safe to operate.
- Have higher efficiency
- Require less maintenance.
- Only fine quality gaseous and liquid fuel can be used as fuel.
- Most of the fuel used in these engines are very costly.
- In comparison with an external combustion engine, the emission is generally high.
- It cannot be used for large scale power generation.
- Due to the detonation of fuel, a lot of noise is generated.
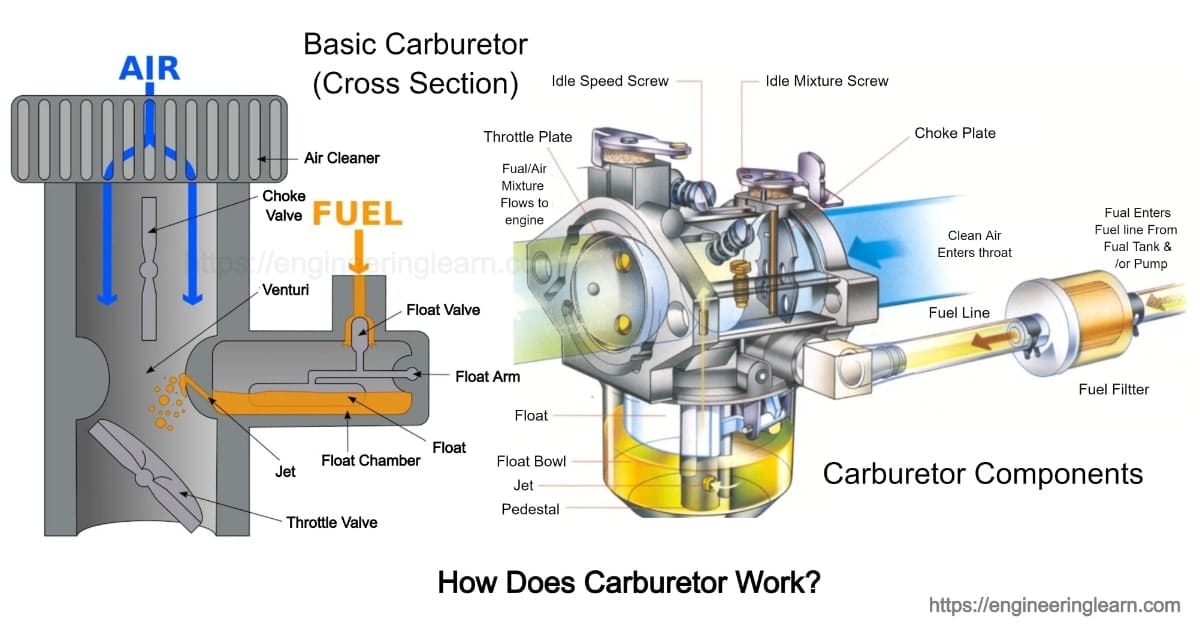
the carburetor is used to mix petrol & air in a specific ratio (15:1) - it works at Bernoulli's principle:
Piston is block like structure used to compress the fuel mixture .
Combustion Thermodynamics focuses on the former physico-chemical phenomena: fuel/air ratios, heating values, maximum work obtainable, exhaust composition, etc., whereas Combustion kinetics focuses on mixing process, flame geometry, ignition, extinction, propagation, stability, etc
combustion modeling is an essential and integral part of modem design/optimization of low-emissions, high-performance combustor.
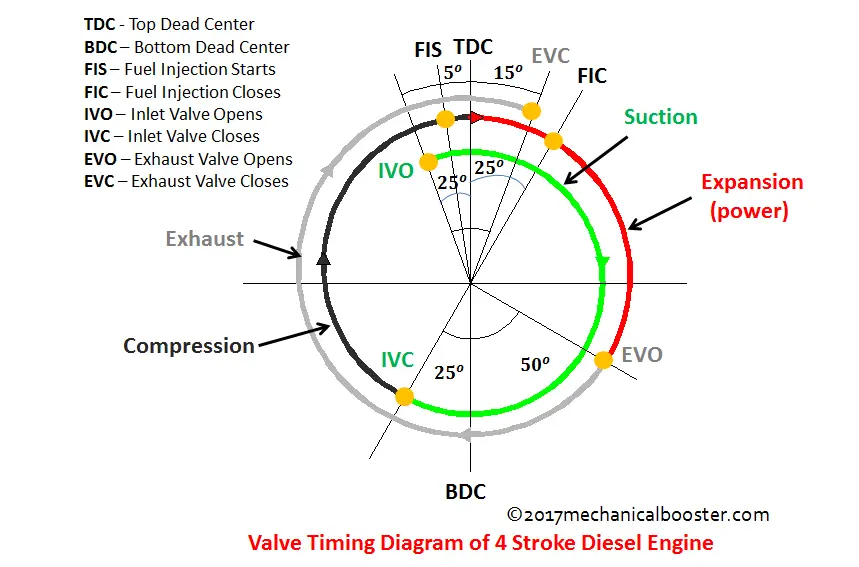
it is a a graphical representation of the opening and closing of the intake and exhaust valve of the engine
the petrol engine is a spark ignition engine consisting of a spark plug for burning of fuel for power stroke .
it is drive shaft mechanism having a crank which converts the reciprocating motion and rotational motion..
Flywheels have the heavy mass used to create the momentum in the engine cycle .=Mn= Mass*Velocity
Ignition lag is the time interval in the process of chemical reaction during which. molecules get heated up to self ignition temperature , get ignited and produce a self. propagating nucleus of flame. The ignition lag is generally expressed in terms of crank.
Petrol / Diesel (high Cetane) / CNG
- 20) What is Technology engine is used in ?
- HYBRID. ...
- DIRECT INJECTION. ...
- VARIABLE VALVE TIMING. ...
- TURBOCHARGING. ...
- CYLINDER DEACTIVATION. ...
- ELECTRIC VEHICLE (EV) ...
- HYDROGEN INTERNAL COMBUSTION ENGINE. ...
- HYDROGEN FUEL CELL.
ndicated power of an engine is given by, I.P = Pim L A N K/60,000
Brake power of an engine is given by, B.P = T. ω
Or, B.P = 2 π NT/60,000
I.P = Indicated Power (kW)
B.P = Break Powder (kW)
Pim = Indicated mean effective pressure (N/m²)
Pbm = Break mean effective Pressure (N/m²)
L = Length of the stroke
A = (πD²/4) = Area of the piston (m²)
N = Number of power strokes
= rpm for 2-stroke engines = rpm/2 for 4-stroke
K = Number of cylinder.
T = Engine Torque (Nm)
F = Force applied to the crank (N)
r = Effective crank radius (m).
ω = Average velocity of crankshaft (rad/sec)
Mechanical Efficiency of Engine: ηmech = B.P/I.P
Otto cycle Efficiency: ηotto = 1- (1/rk ɤ - 1)
Diesel cycle Efficiency: [1 - (1/ɣ). (1/rk ɤ - 1)] x [(rcɤ - 1)/rc - 1)]
Where, rk = v₁/v₂ = Compression ratio
re = v₄/v₃ = Expansion ratio
rc = v₃/v₂ = Cut-off ratio
Also, rk = re x rc.