The Engine Systems -Explained
Engine Inlet system
The air intake system of modern automobiles consists of three main parts: the air filter, the mass flow sensor and the throttle body. Some modern intake systems are quite complex and often include specially designed intake manifolds to optimally distribute air and air/fuel mixtures to each cylinder.
components
- Primary filter
- Secondary filter
- Fuel filter
- Carburetor
- FIP
- Injector
- Inlet valve
Engine Exhaust system
Exhaust systems are used to keep reactive exhaust gases away from controlled combustion in an engine or furnace. The overall system carries combustion gases from the engine and includes one or more exhaust pipes.
Component
- Manifold. ...
- Flex Pipe. ...
- Catalytic Converters. ...
- Oxygen (O2) Sensors. ...
- Isolators/Gaskets/Clamps. ...
- Resonator Assemblies/Pipe Accessories. ...
- Mufflers/Muffler Assemblies.
Engine Lubrication system
Lubrication is the application of a substance such as oil or grease to an engine or component to minimize friction and enable smooth movement. A lubrication system is a mechanical system for lubricating an internal combustion engine, where a pump forces oil into the engine's bearings.
The cooling system has four main functions: Removes excess heat from the engine, maintains a constant engine operating temperature, raises the temperature of a cold engine as quickly as possible, and provides an opportunity for heating operation (heats the cabin)
Engine Cooling System
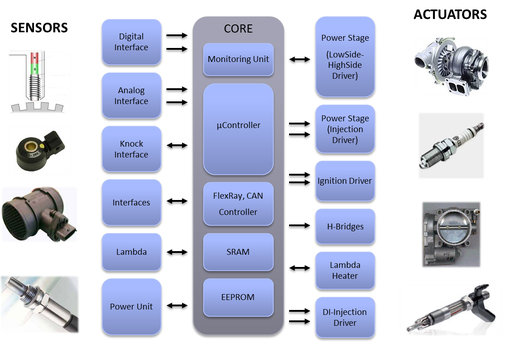
Engine Management System.
engine management system is a common engine control unit that can be used as an 'open' EMS system to operate all types of internal combustion engines during performance and emissions development. In addition, RPEMS controls the complete vehicle functions and can run ICE and electric powertrain configurations for prototype performance and functional verification testing.